
In addition, the features at pre- and postprocedural MRI will be discussed to help ensure that diagnostic radiologists may be of greatest use to the ordering physicians. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is presently the study of choice for assessment of the internal auditory canal (IAC). Bilateral 77059 Brachial Plexus 71550 / 71552. The purpose of this review is to provide an overview of the most useful MRI sequences for internal auditory canal and labyrinthine imaging, review the relevant anatomy, and discuss the expected appearances of the most commonly encountered pathologic entities. Nevertheless, despite the widespread use of MRI for these purposes, many radiologists remain unfamiliar with the complex anatomy and expected imaging findings with such examinations. It is also extensively used in pre- and postoperative evaluations, particularly in patients with vestibular schwannomas and candidates for cochlear implantation. If a family of CPT codes is not listed in this matrix, an exact match is required between. Excision soft tissue lesion, external auditory canal : 69205. Excision exostosis(es), external auditory canal : 69145. Excision external ear partial, simple repair : 69140.
#Internal auditory canal mri cpt code code#
It is used to evaluate normal anatomic structures, evaluate for vestibular schwannomas, assess for inflammatory and/or infectious processes, and detect residual and/or recurrent cholesteatoma. the loinc/radlex committee agreed to use a subset of the two-letter dicom modality codes as the primary modality identifier. CPT Code Description Auditory System 69100.
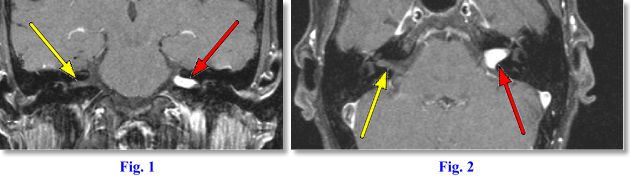
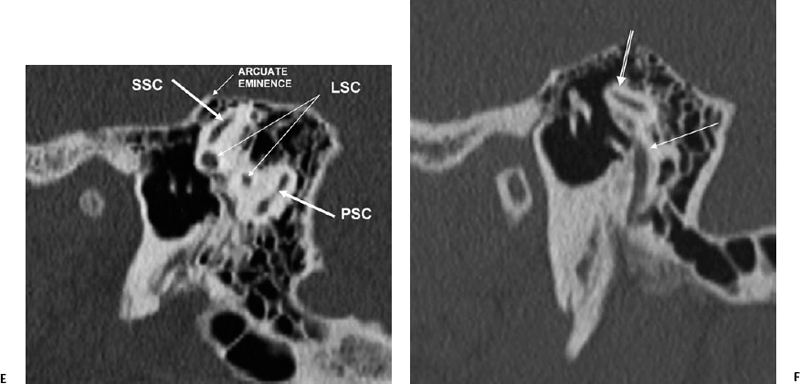
(MRI) utilizes magnet and radio waves to produce diagnostic images that allow a doctor to visualize the hips. MRI is firmly established as an essential modality in the imaging of the temporal bone and lateral skull base. The internal auditory canal (IAC) is a channel in the petrous bone located between the porus acousticus (medial) and the fundus (lateral)(17).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
